Why Tooth Surface Texture Affects Bacteria Retention-3251m ago
-3251m ago
Bacterial retention in the oral cavity is not random — it is strongly influenced by the microscopic texture of tooth surfaces. Even minor variations in enamel smoothness, wear patterns, restorations, or hygiene habits can significantly alter how plaque biofilms adhere and mature. Rough or irregular surfaces create niches that shelter microorganisms from mechanical removal and saliva flow, accelerating plaque accumulation and disease risk. This article explores the scientific relationship between tooth surface texture and bacterial colonization, the clinical implications for oral health, and evidence-based strategies to minimize retention through optimized brushing and precision-guided oral care.
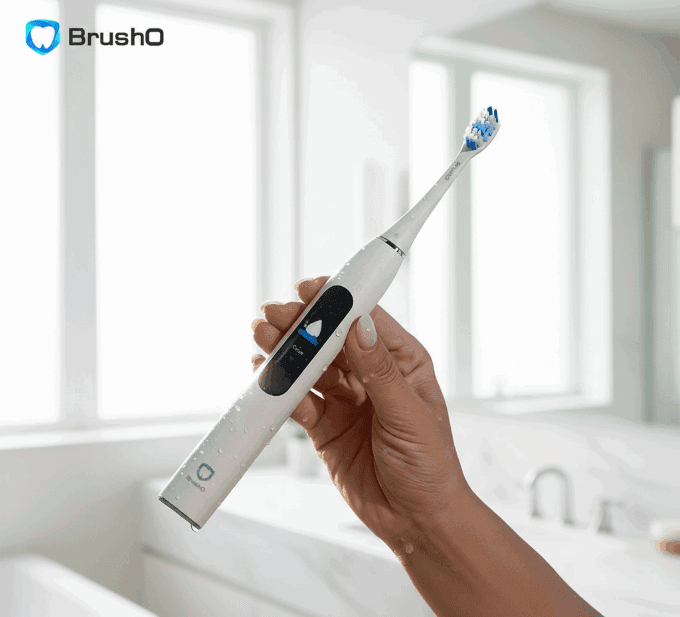

Understanding Tooth Surface Texture
Tooth surfaces appear smooth to the naked eye, yet at a microscopic level, they contain ridges, grooves, and pores shaped by:
• Enamel mineral structure
• Wear and abrasion
• Acid erosion
• Dental restorations
• Orthodontic alignment
• Natural anatomy of pits and fissures
These microtopographical variations influence bacterial adhesion patterns and plaque retention behavior.
How Bacteria Attach to Tooth Surfaces
Biofilm Formation Mechanics
Oral bacteria adhere through a multistage process:
1. Salivary proteins form a pellicle coating
2. Microorganisms bind to the pellicle
3. Colonies multiply and produce extracellular matrix
4. Mature plaque biofilm develops
Surface irregularities enhance attachment stability during early colonization.
The Role of Surface Roughness
Research in dental materials science shows rougher textures:
• Increase bacterial anchoring points
• Reduce shear removal during brushing
• Protect microbes from saliva cleansing
• Accelerate biofilm maturation
Even micrometer-level roughness differences can significantly influence plaque retention rates.
Sources of Surface Roughness
Natural Anatomical Features
• Deep occlusal grooves
• Developmental pits
• Molar fissures
These areas inherently trap bacteria.
Mechanical Wear
• Aggressive brushing
• Bruxism
• Dietary abrasion
These can create uneven enamel patterns.
Chemical Erosion
• Acidic foods and drinks
• Gastric reflux
• Low oral pH
Erosion alters enamel morphology, increasing microbial adherence.
Dental Restorations
Fillings, crowns, and bonding materials may present microtexture variations depending on finishing quality.
Clinical Consequences of Increased Bacterial Retention
Persistent microbial colonization elevates risk for:
• Cavities
• Gingival inflammation
• Periodontal disease
• Halitosis
• Enamel demineralization
Localized plaque retention frequently correlates with anatomical surface irregularities.
Why Traditional Brushing May Miss Texture-Driven Risk Zones
Manual brushing limitations include:
• Uneven pressure application
• Incomplete zone coverage
• Difficulty accessing fissures
• Lack of surface feedback
Users cannot visually detect microtopographical plaque accumulation.
How Precision Brushing Technology Helps
AI-guided toothbrush systems like BrushO support the mitigation of texture-related bacterial retention by:
• Monitoring coverage across complex surfaces
• Tracking zone consistency
• Detecting insufficient cleaning pressure
• Encouraging systematic brushing patterns
• Providing behavioral feedback via reports
Such precision guidance enhances removal effectiveness in high-retention regions.
Strategies to Reduce Surface-Based Plaque Retention
Mechanical Techniques
• Angled brushing toward fissures
• Full-zone rotation patterns
• Adequate brushing duration
Chemical Support
• Fluoride strengthening
• Remineralizing agents
• Antimicrobial rinses
Professional Care
• Regular polishing
• Sealants for deep grooves
• Surface smoothing procedures
Technology Integration
• Coverage analytics
• Pressure regulation
• Habit tracking
Long-Term Oral Health Implications
Managing bacterial retention on textured surfaces contributes to:
• Lower plaque accumulation
• Reduced cavity risk
• Improved gum stability
• Balanced microbiome ecology
• Extended tooth longevity
Understanding surface science enhances preventive care precision.
Tooth surface texture plays a fundamental role in bacterial retention and plaque ecology. Microscopic irregularities act as anchoring sites that influence biofilm formation, disease progression, and hygiene effectiveness. Because these features are invisible to the user, improving cleaning accuracy through a structured technique and intelligent feedback becomes essential. By combining surface-aware brushing strategies with precision-guided technologies such as AI-assisted monitoring, individuals can reduce microbial persistence and strengthen long-term oral health outcomes.
The Hidden Role of Saliva Enzymes in Oral Defense
-7561m ago
Do Small Brushing Gaps Lead to Big Dental Costs?
-3246m ago
Recent Posts
Why Your Saliva Flow Changes Throughout the Day
Saliva flow fluctuates throughout the day due to circadian rhythm, hydration, diet, and stress. Learn why it matters for oral health and how smart brushing protects teeth during low-saliva periods.
How Oral Muscle Tension Influences Tooth Wear
Oral muscle tension and jaw strain can accelerate tooth wear, enamel erosion, and gum stress. Learn how muscle habits influence dental health and how smart brushing supports long-term protection.
How Breathing Habits Affect Your Face And Oral Health
Discover how mouth vs nose breathing affects oral health, facial development, jaw alignment, and sleep quality — and how to protect your teeth and gums with proper habits.
Brushing More Than Twice a Day Is Helpful or Harmful?
Is brushing more than twice daily good for your teeth? Learn how brushing frequency affects enamel, gums, and sensitivity, and discover dentist-backed guidance for safe oral care habits.

What Does Eating Sugar at Midnight Do to Your Mouth?
Discover how eating sugar at midnight affects oral bacteria, enamel health, and overall wellness. Learn why late-night snacking raises cavity risk and how proper brushing protects your teeth.

How Brushing Confidence Shapes Oral Health Outcomes
Discover how brushing confidence influences oral health outcomes, plaque control, and gum protection. Learn why self-efficacy in brushing technique matters and how smart toothbrush feedback improves long-term dental health.

Why Inconsistent Sleep Schedules Harm Gum Recovery
Irregular sleep schedules can slow gum recovery, worsen inflammation, and disrupt oral microbiome balance. Learn how sleep affects periodontal health and how smart brushing habits help protect your gums.

Why People With the Same Brush Get Very Different Results
Discover why two people using the same toothbrush can experience different oral health results. Learn how technique, pressure, coverage, and AI-guided brushing influence outcomes.

How Habit Loops Control Your Oral Health
Learn how habit loops shape your oral health and brushing consistency. Discover the neuroscience behind oral hygiene routines and how AI-guided tools like BrushO strengthen healthy dental behaviors.
Why Your Brain Fights Against Good Brushing Habits
Discover why your brain resists consistent brushing habits and how behavioral science, habit formation, and AI-guided tools like BrushO can improve oral hygiene consistency.
